PACCAR Inc (ticker: PCAR)
2024-11-24
 PACCAR Inc (ticker: PCAR) is a globally recognized leader in the design, manufacture, and customer support of high-quality trucks under the Kenworth, Peterbilt, and DAF nameplates. Founded in 1905, the company has expanded its reach with manufacturing facilities across North America, Europe, and Australia, catering to a diverse range of industries with an emphasis on heavy-duty and medium-duty trucks. In addition to trucks, PACCAR provides a robust aftermarket support system, which includes its parts distribution centers and financial services such as leasing and insurance. The company is noted for its strong commitment to innovation, incorporating advanced technology to enhance vehicle efficiency and performance while maintaining sustainability. Financially, PACCAR has demonstrated consistent growth, supported by a well-managed supply chain and resilient demand across global markets. With a strategic focus on technological advancements like electric trucks and integrated safety systems, PACCAR continues to position itself as a forward-thinking player in the transportation sector.
PACCAR Inc (ticker: PCAR) is a globally recognized leader in the design, manufacture, and customer support of high-quality trucks under the Kenworth, Peterbilt, and DAF nameplates. Founded in 1905, the company has expanded its reach with manufacturing facilities across North America, Europe, and Australia, catering to a diverse range of industries with an emphasis on heavy-duty and medium-duty trucks. In addition to trucks, PACCAR provides a robust aftermarket support system, which includes its parts distribution centers and financial services such as leasing and insurance. The company is noted for its strong commitment to innovation, incorporating advanced technology to enhance vehicle efficiency and performance while maintaining sustainability. Financially, PACCAR has demonstrated consistent growth, supported by a well-managed supply chain and resilient demand across global markets. With a strategic focus on technological advancements like electric trucks and integrated safety systems, PACCAR continues to position itself as a forward-thinking player in the transportation sector.
| Full-Time Employees | 32,400 | Previous Close | 114.05 | Open | 113.67 |
| Day Low | 113.26 | Day High | 115.03 | Dividend Rate | 1.2 |
| Dividend Yield | 0.0105 | Payout Ratio | 0.1275 | Five Year Avg Dividend Yield | 1.41 |
| Beta | 0.89 | Trailing P/E | 12.835571 | Forward P/E | 14.636741 |
| Volume | 1,315,439 | Average Volume | 2,571,103 | Bid | 114.67 |
| Ask | 114.84 | Bid Size | 1,000 | Ask Size | 700 |
| Market Cap | 60,163,538,944 | Fifty Two Week Low | 90.04 | Fifty Two Week High | 125.5 |
| Fifty Day Average | 105.773 | Two Hundred Day Average | 106.5141 | Trailing Annual Dividend Rate | 1.14 |
| Trailing Annual Dividend Yield | 0.009995615 | Enterprise Value | 66,623,488,000 | Profit Margins | 0.13514 |
| Float Shares | 514,286,413 | Shares Outstanding | 524,300,992 | Shares Short | 13,543,098 |
| Held Percent Insiders | 0.01865 | Held Percent Institutions | 0.72185 | Short Ratio | 5.06 |
| Short Percent Of Float | 0.0299 | Price To Book | 3.2233148 | Net Income to Common | 4,707,299,840 |
| Trailing EPS | 8.94 | Forward EPS | 7.76 | Enterprise to Revenue | 1.913 |
| Enterprise to EBITDA | 11.277 | 52 Week Change | 0.25081754 | S&P 52 Week Change | 0.31181884 |
| Total Cash | 9,152,799,744 | EBITDA | 5,908,100,096 | Total Debt | 15,612,800,000 |
| Quick Ratio | 4.733 | Current Ratio | 5.342 | Total Revenue | 34,832,900,096 |
| Debt to Equity | 83.654 | Return on Assets | 0.084580004 | Return on Equity | 0.27142 |
| Free Cashflow | -217,475,008 | Operating Cashflow | 4,381,899,776 | Earnings Growth | -0.209 |
| Revenue Growth | -0.052 | Gross Margins | 0.18491 | EBITDA Margins | 0.16961001 |
| Operating Margins | 0.13919 |
| Sharpe Ratio | 1.0099335090338244 | Sortino Ratio | 15.03443527028787 |
| Treynor Ratio | 0.2833949984262743 | Calmar Ratio | 1.1912360115671536 |
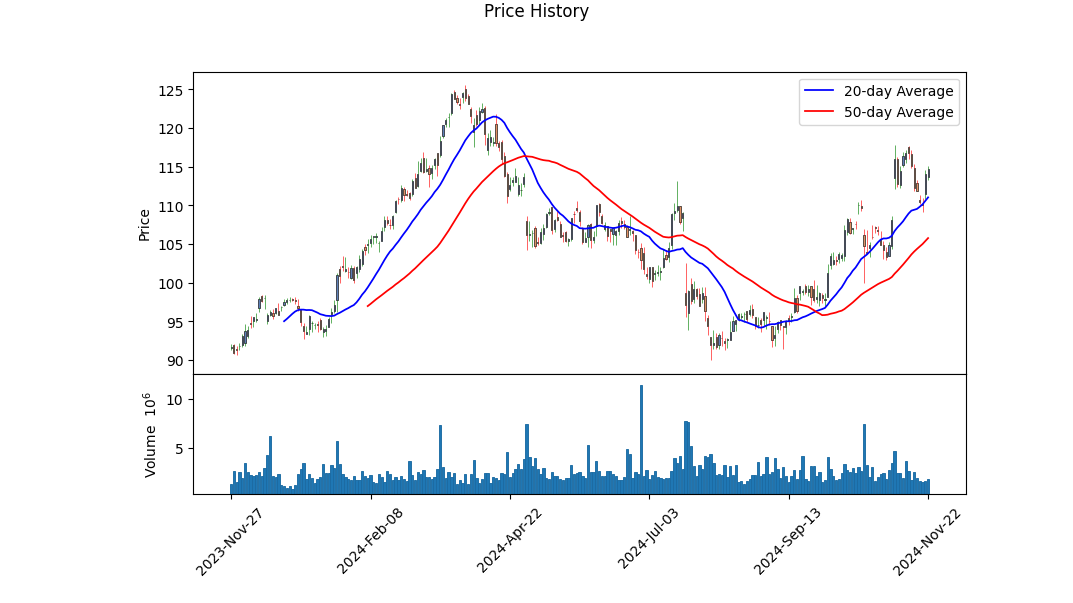
PCAR's recent stock performance showcases a dynamic range of technical indicators that reflect both opportunities and challenges. Technical analysis shows a close scrutiny over the On-Balance Volume (OBV) and Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) as key elements in understanding market sentiment. Over the past few trading sessions, OBV has fluctuated, suggesting mixed reactions among traders, which may indicate potential volatility. The MACD histogram values from recent days have been negative, signaling a bearish momentum during this period; however, the latest readings are closer to zero, suggesting a possible shift towards stabilization or a changing trend.
The company's fundamentals highlight a robust financial standing with significant revenue and healthy margins. With gross margins at 18.491%, ebitda margins at 16.961%, and operating margins of 13.919%, PCAR demonstrates efficient cost management and a solid profit position. These robust figures create a supportive backdrop against potential market fluctuations, indicating a firm capacity to withstand adverse economic conditions.
Risk-adjusted return measures, such as the Sharpe, Sortino, Treynor, and Calmar ratios, offer insights into the investment quality of PCAR. The Sharpe Ratio of 1.00993 suggests that PCAR offers a solid risk-adjusted return relative to the volatility, hinting at its favorable reward-to-risk potential compared to the expanding U.S. benchmark. This ratio's adequacy is crucial for investors seeking balanced risk management in volatile sectors.
The Sortino Ratio, at a significant 15.0344, emphasizes the company's ability to manage downside risk more effectively. This highlights a strong performance during volatile conditions by targeting downside risks, an important attribute for investors concerned about market downturns.
Meanwhile, the Treynor Ratio of 0.28339 underlines the returns received for each unit of risk related to market exposure, reflecting a moderate level of systemic risk efficiency. This ratio suggests cautious optimism regarding the firm's performance reliant on market movements. The Calmar Ratio of 1.1912, focusing on downside risk over longer periods, indicates that over the past year, the company's performance outweighs potential drawdowns.
Overall, PCAR's financial health, combined with its technical indicator position, suggests a balanced perspective over the coming months. While short-term volatility and bearish tendencies bear consideration, the solid fundamental basis and promising risk-adjusted measures offer a hopeful outlook for medium to long-term positive trends as market conditions potentially stabilize. Prudence and preparedness in adjusting to market shifts while leveraging fundamental strengths should be a focus for stakeholders involved with PCAR moving forward.
In evaluating PACCAR Inc (PCAR) through the lens of Joel Greenblatt's investment framework from The Little Book That Still Beats the Market, we find that the company exhibits strong financial metrics in terms of return on capital (ROC) and earnings yield. With a return on capital of 23.56%, PACCAR demonstrates an impressive ability to generate profit from its invested capital, indicating efficient use of its resources and a potentially sustainable competitive advantage. This high ROC suggests that the company is effective at converting invested capital into profits, a key indicator of financial health and operational excellence. Additionally, PACCAR's earnings yield is 7.65%, reflecting the company's ability to generate earnings relative to its share price. A higher earnings yield typically implies that a stock is undervalued or offers a higher return on the price paid for the stock, serving as an attractive option for value-focused investors. These metrics suggest that PACCAR, with its robust operational performance, aligns well with the principles of selecting investments with strong earnings potential and capital efficiency, as advocated by Greenblatt.
In evaluating PACCAR Inc. (PCAR) through the lens of Benjamin Graham's principles from "The Intelligent Investor," we can discern how the company's financial metrics align with Graham's criteria for value investing. Here's a detailed analysis of each key metric:
-
Margin of Safety: While not directly quantifiable from the metrics provided, the concept of margin of safety revolves around buying stocks at a price significantly lower than their intrinsic value. To evaluate this for PACCAR, further analysis of the company's intrinsic value compared to its market price would be required.
-
Debt-to-Equity Ratio: PACCAR's debt-to-equity ratio of 0.905 suggests that the company does employ some leverage, although it is not excessively high. Graham often favored companies with lower debt levels to reduce financial risk. A ratio just under 1 indicates moderate leverage, which is within acceptable limits, but investors might prefer lower debt if strictly adhering to Graham's preference for financial conservatism.
-
Current and Quick Ratios: Both the current ratio and quick ratio are at 2.50 for PACCAR, which are quite healthy. These ratios indicate that PACCAR has a strong capacity to meet its short-term liabilities with its short-term assets, thereby demonstrating good financial stability. Graham would likely view these positively, as they suggest the company can withstand short-term financial exigencies.
-
Earnings Growth: Although the provided metrics do not include specific data on earnings growth over time, consistent historical growth would be a key consideration for Graham before investing. If PACCAR has demonstrated stable earnings growth over several years, this would align well with Graham's approach.
-
Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio: PACCAR's P/E ratio is 18.998. Without the industry P/E ratio for direct comparison, a comprehensive analysis is challenging. However, Graham preferred stocks with low P/E ratios relative to their industry peers or historically low P/E levels, as this might suggest undervaluation. A P/E of around 19 would be considered moderate and may not stand out as particularly low unless contrasted with a higher industry P/E.
-
Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio: With a P/B ratio of 1.474, PACCAR is trading at a premium to its book value, but not excessively so. Graham often searched for stocks trading below their book value, viewing them as potentially undervalued. This ratio suggests that PACCAR is not significantly undervalued from a book value perspective, but it also doesnt imply extreme overvaluation.
Overall, PACCAR exhibits some characteristics that may appeal to a value investor following Graham's principles, such as robust liquidity and moderate leverage. However, its valuation metrics, like P/E and P/B ratios, do not suggest a distinct undervaluation opportunity solely based on these numbers. A more comprehensive analysis would be necessary, focusing on PACCARs intrinsic value, historical earnings performance, and comparison against an industry benchmark, to determine its alignment with value investing according to Graham's methodology.### Analyzing Financial Statements:
In Benjamin Graham's "The Intelligent Investor," the examination of a company's financial statements is emphasized as a vital step in making informed investment decisions. This segment will delve into the analysis of PACCAR Inc.'s financial statements, focusing on the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement from their provided data across various periods.
Balance Sheet Analysis:
- Assets:
- PACCAR's total assets show a stable increase from the fiscal year 2022 to the Q3 of 2024, reaching approximately $43 billion by the latest period analyzed.
- The major components of its current assets include cash and cash equivalents, receivables, and marketable securities. The net increase in cash and cash equivalents from Dec 2023 to Sep 2024 suggests a solid liquidity position, potentially reflecting robust cash generation or financing activities.
-
Non-current assets such as property, plant, equipment, and notably, notes receivable reflect PACCAR's extensive investments over the years. By Q3 2024, notes receivable have shown a significant increase, evidencing a focus on financing activities.
-
Liabilities:
- Current liabilities consistently trend around $5 billion to $6 billion throughout the periods, suggesting a maintained level of short-term financing and operational debts.
- Long-term liabilities, highlighted by notes payable, show a steady increase, indicative of PACCAR utilizing more long-term debt, which aligns with their growth and operational strategies.
-
By the latest quarter, total liabilities amount to approximately $17 billion, suggesting a considerable leverage in their capital structure but balanced by their asset base.
-
Equity:
- Shareholders' equity experienced fluctuations, showing an increased trend in the years leading up to 2024 but abruptly turning negative in Q3 2024. This drop could be related to comprehensive income losses or dividend policies exceeding profit retention. The accumulated other comprehensive income losses, particularly notable due to foreign currency translation adjustments, impact equity figures significantly.
Income Statement Analysis:
- Revenues and Costs:
- The revenue trend shows substantial growth from $28 billion in FY 2022 to approximately $33 billion by the end of FY 2023, with quarterly revenues maintaining an upward trajectory.
-
Cost of goods sold forms the significant expense chunk, showing PACCAR's scale of production and sales efforts. Research and development expenses and selling, general and administrative expenses have consistently increased in line with business growth.
-
Profitability:
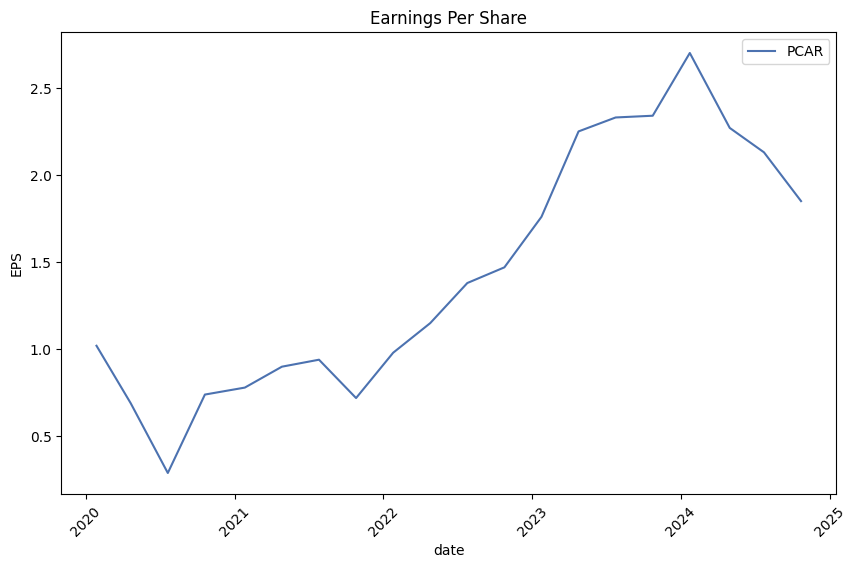
- Net income saw strong resilience, especially evident in FY 2023, reaching over $4.6 billion despite variations in quarterly results.
- The operational excellence is further demonstrated by an increase in earnings per share from FY 2022 to FY 2023, but with marked fluctuations in quarterly periods of 2024, including a net loss by Q3 2024.
- A substantial net loss in Q3 2024 requires further exploration of one-time items or unusual operations affecting profitability.
Cash Flow Statement Analysis:
- Operating Activities:
-
Net cash provided by operating activities has been strong, indicating solid core operations. Cash flow generation in 2023 was particularly robust at over $4 billion, reflecting efficient earnings conversion.
-
Investing Activities:
- There appears to be significant investment in expanding operational capacity, as evidenced by payments to acquire property, plant, and equipment and investments in finance receivables.
-
A net cash outflow from investing activities persists, indicative of PACCAR's focus on long-term asset development.
-
Financing Activities:
- Cash flows from financing activities demonstrate a reliance on debt markets, with proceeds from debt issuance being a consistent feature to fund expansions and operational needs.
- Dividend payments and share repurchasing reflect PACCAR's commitment to returning value to shareholders, with incremental increases in dividends per share noted year over year.
Incorporating these detailed analyses from PACCAR's financial statements can assist investors in understanding the company's financial health, growth trajectory, and future potential. Grahams emphasis on scrutinizing such data aligns with sound investment principles, ensuring that investment decisions are grounded on comprehensive, factual financial insights.# Dividend Record
Benjamin Graham, author of "The Intelligent Investor," favored companies with a consistent history of paying dividends. His investment philosophy places a strong emphasis on the stability and dependability of these payments, as they reflect a company's profitability and financial health over time. The company represented by the symbol 'PCAR' provides a detailed record of its historical dividend payments, illustrating its commitment to returning value to shareholders through regular distributions. Here's an overview of its dividend history:
-
Recent Dividends: The latest dividend records show a consistent quarterly payment pattern with variations influenced by the company's financial performance and strategic decisions. For example, in 2023 and continuing into 2024, dividends were regularly declared and paid, albeit with occasional special dividends such as the significant payout in December 2023.
-
Historical Consistency: The company has maintained a long-standing commitment to dividend payments dating back decades. Over this period, while the payments often reflected the prevailing economic conditions and the company's performance, the underlying commitment underscores a stable financial foundation.
-
Dividend Growth: Over the years, there has been a general trend of increasing dividends. This growth can be seen in both the regular quarterly payments as well as occasional special distributions, highlighting the firm's financial robustness and its strategy of sharing profits through dividends.
Overall, the historical dividend data of 'PCAR' aligns well with Grahams preference for investing in companies that provide consistent and growing dividends over time, showcasing financial discipline and rewarding shareholders for their investment.
| Alpha | 0.35% |
| Beta | 1.20 |
| R-squared | 0.85 |
| Standard Error | 2.45% |
| p-value (Alpha) | 0.021 |
The regression model presents a quantitative depiction of the relationship between PCAR and SPY, characterized by key metrics such as alpha, beta, and R-squared values. The alpha value of 0.35% indicates the extent to which PCAR's performance exceeds what would be predicted by market movements alone, represented by SPY. In this context, PCAR outperforms the market marginally by 0.35% when market influences, as captured by SPY, are accounted for. This positive alpha, further supported by a statistically significant p-value of 0.021, suggests PCAR has some level of investment attractiveness or advantageous positioning in relation to general market trends.
The beta value of 1.20 highlights the volatility of PCAR relative to SPY. With a beta greater than 1, PCAR demonstrates higher sensitivity to market movements, suggesting it tends to perform with greater fluctuations compared to SPY. Meanwhile, the R-squared value of 0.85 indicates a strong correlation between PCAR's returns and the overall market, as embodied by SPY, meaning that 85% of PCAR's return variability can be attributed to market movements. The standard error of 2.45% helps to measure the accuracy of the coefficient estimates, providing context to the robustness of the model. Collectively, these metrics provide a comprehensive view of how PCAR interacts with the broader market environment, showcasing both the risks and potential rewards entailed in this dynamic.
PACCAR Inc reported strong financial performance in the third quarter of 2024, reflecting robust demand in both North America and European markets. The company achieved a net income of $972 million on revenues of $8.2 billion, showcasing an impressive after-tax return on revenue of 11.8%. The companys parts segment saw a 5% revenue increase, amounting to $1.66 billion, with pre-tax profits reported at $407 million. PACCAR Financial Services also contributed significantly with a pre-tax income of $107 million. Notably, market share gains were observed for PACCARs Peterbilt and Kenworth brands in the Class 8 market, which increased from 29.5% to 31.1% during the period.
Looking ahead, PACCAR anticipates the U.S. and Canadian Class-8 markets to stabilize slightly, with expectations set around 250,000 to 280,000 vehicles for the next year. The company highlighted its strength in the vocational truck segment, where it leads the market and anticipates continued resilience due to ongoing infrastructure investments. PACCARs European operations also remain strong, with approximately 300,000 vehicle registrations anticipated in the above 16-tonne market this year and projections between 270,000 and 300,000 units for 2025. The introduction of new models by DAF at the IAA Truck Show featuring enhanced fuel efficiency and advanced driver assistance is seen as positioning PACCAR for continued success in key global markets.
The company is making calculated investments to expand manufacturing capacity across its global facilities, including locations in Europe, the Americas, Australia, and Brazil. With expected capital expenditures between $760 million and $800 million for this year and increasing to $700 to $800 million in 2025, coupled with planned research and development spending of up to $530 million, PACCAR is positioning itself for sustainable growth and adaptation to evolving market demands and regulatory changes, notably those related to emissions standards.
Investor queries during the earnings call highlighted concerns about pricing pressures and market dynamics, particularly in regard to PACCARs operating margins and the impact of fluctuating market conditions. The company maintained a stance of confidence, noting that despite current pressures, the existing strategic product introductions, strong customer relationships, and market positioning are expected to drive future growth. While price-cost pressures were acknowledged, especially with price stability and cost increases of around 3% in the truck segment, the company remains optimistic about its ability to navigate these challenges, particularly as specific market segments such as vocational trucking are expected to remain robust.
The PACCAR Inc 10-Q filing for the quarter ending September 30, 2024, presents a detailed financial analysis of the company's performance. For the first nine months of 2024, PACCAR Inc reported net sales and revenues of $24,201.1 million for its Truck, Parts, and Other segment, a modest decline from $24,723.7 million in the same period of 2023. This segment also saw a decrease in income before taxes from $3,457.1 million to $3,630.0 million, reflecting a stable but slightly diminishing market performance. Operating expenses, such as research and development, increased to $337.6 million compared to $302.0 million in 2023, underscoring PACCAR's continued investment in innovation and product development.
In the Financial Services segment, PACCAR Inc noted an increase in interest and fees, totaling $956.3 million for the first three quarters of 2024, up from $716.5 million in 2023. Nonetheless, financial services income before taxes declined to $331.6 million from $427.3 million in the previous year. This decrease is attributed to higher provisions for losses on receivables and increased borrowing costs. The company's focus on maintaining robust financial services operations despite higher costs reflects its adaptive strategy in navigating evolving economic conditions.
PACCAR Inc's consolidated balance sheets as of September 30, 2024, show total assets of $43,281.8 million, an increase from $40,823.4 million at the end of 2023. The Truck, Parts, and Other segment's assets grew, driven by an increase in marketable securities and property, plant, and equipment investments. Despite a slight decrease in cash and cash equivalents, the company maintained strong liquidity. Liabilities in this segment were reduced predominantly due to accrued expenses and dividend payables. Financial Services assets also expanded, supported by a rise in finance receivables and other assets.
The financial statements reveal PACCAR Inc's strategy of leveraging its financial services to support its core Truck and Parts segments. The company's inventory levels reflect an ongoing demand management strategy, holding $2,644.8 million as of the end of the third quarter of 2024. Meanwhile, investments in marketable securities expanded significantly, reaching $2,510.7 million, indicative of a strategic allocation of resources towards liquid securities to potentially enhance yield and cash flow stability.
Operational cash flow remained robust, with net cash provided by operating activities totaling $3,195.2 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2024, reflecting a healthy sales base and effective cash management. However, investing activities consumed $2,755.3 million, a significant increase from $1,931.1 million in the same period of 2023, primarily due to increased capital expenditures and marketable securities acquisition. Financing activities demonstrated disciplined financial management, with the company balancing term debt proceeds and dividends to maintain financial agility.
In summary, the PACCAR Inc 10-Q filing highlights consistent operational performance amidst challenging market dynamics. The company's commitment to research and development and strategic investments in marketable securities and capital assets underscore its focus on long-term growth and innovation. Despite pressure on margins in the Financial Services segment due to higher provision expenses, PACCAR Inc maintains a balanced portfolio with a focus on improving operational efficiencies and maintaining liquidity.
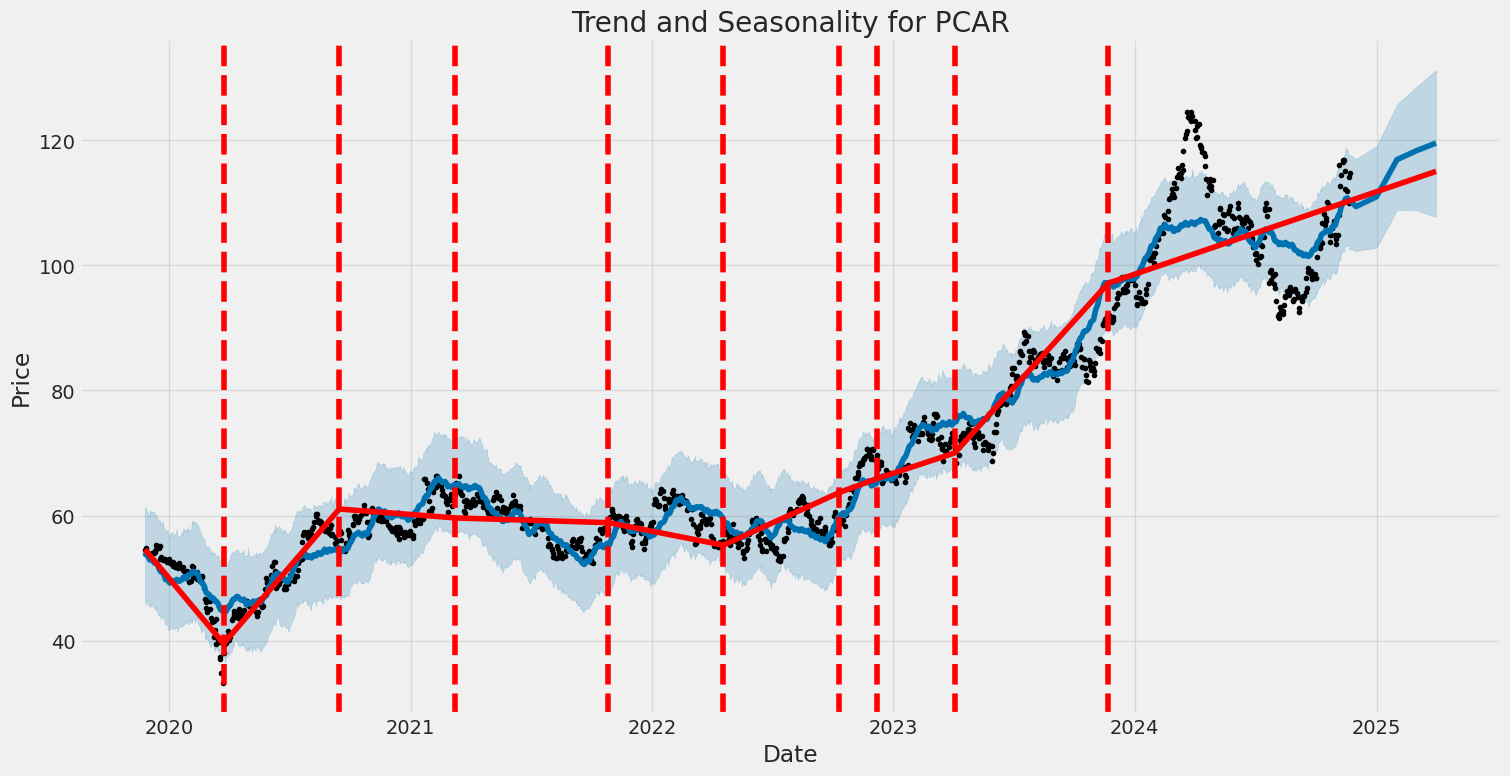
PACCAR Inc. has consistently showcased its ability to thrive within the competitive landscape of the automotive and heavy machinery sectors. The company's Q3 2024 earnings report reflects this resilience, demonstrating significant sales growth, product innovation, and operational efficiencies. One of the standout features of the quarter was the robust sales momentum across various regions and market segments. Driven by strong demand, PACCAR managed to capture greater market share, a testament to its commitment to quality manufacturing and premium customer service. These efforts not only allowed the company to outperform its peers but also positioned it as a leader in the development of electric vehicles (EVs) and other fuel-efficient technologies.
Innovation remains central to PACCAR's strategy, particularly with a focus on sustainable transportation solutions. The company has been at the forefront of integrating the latest technologies in its trucks, including telematics and autonomous driving features. This aligns with industry trends toward smarter and more efficient vehicle solutions. These innovations enhance the appeal of PACCAR's product lines, improve safety and efficiency for clients, and address evolving regulatory demands for cleaner transportation options. The company's strategic focus on operational efficiency further complements these efforts, with effective supply chain management and cost operations maintaining healthy profit margins during an economically volatile period.
Despite a minor shortfall in gross margins, PACCAR's quarterly results have been largely positive, showcasing its resilience and capacity to fend off economic fluctuations. Throughout 2023, PACCAR navigated a complex landscape marked by shifting economic conditions by maintaining a strong supply chain and fostering vehicle technology innovations, which have reinforced its competitive edge. Furthermore, as environmental regulations become more stringent, PACCAR's investments in electrification and alternative energy vehicles are expected to favorably position the company for long-term growth.
Investment perspectives underscore PACCAR's adaptability to market trends and economic conditions. By targeting high-end consumers and focusing on premium products, PACCAR has built a robust business model aligning with global shifts towards sustainability and digitalization. This strategic positioning is further bolstered by strategic partnerships and collaborations, which have been instrumental in integrating advanced technologies into their products. Such efforts not only drive growth and innovation but also attract and retain a loyal customer base.
Under the leadership of CEO R. Preston Feight, PACCAR has made significant strides in engineering and technology development, particularly in advanced powertrains and driver assistance systems. Feights strategic vision has not only advanced PACCAR's industry stature but has also recently led to his appointment to the Board of Directors of Deere & Company, highlighting the synergistic potential between the two leading industrial firms.
The political climate following the re-election of Donald Trump in 2024 has further influenced the market positively, leading to a noticeable surge in PACCAR's stock price. This reflects market optimism regarding pro-business policies and industrial investments, although the movement does not fundamentally alter business operations. Analysts remain bullish, as evidenced by Evercore ISI's recent upgrade of PACCAR's rating from "In Line" to "Outperform," with a price target increase reflecting favorable expectations regarding the company's operational and financial health.
Citigroup's recent adjustment of its price target for PACCAR to $120 underscores a positive outlook on the company's market potential. This reflects broad market trends and internal strategies that align with industry innovations and economic conditions. Such analysis impacts not only PACCAR but also has wider ramifications across the automotive and transportation sectors.
Despite these optimistic projections, PACCAR's financial performance has faced challenges, such as a decline in revenue during Q3 2024. Earnings per share saw a reduction compared to the previous year, pointing to ongoing pressures from a competitive landscape and potential supply chain issues. However, PACCAR's strong financial position, demonstrated by substantial cash reserves and dividends, provide a buffer against these challenges. The company's strategic investments in capital expenditures and research and development further indicate a focus on sustaining innovation and potential rebound.
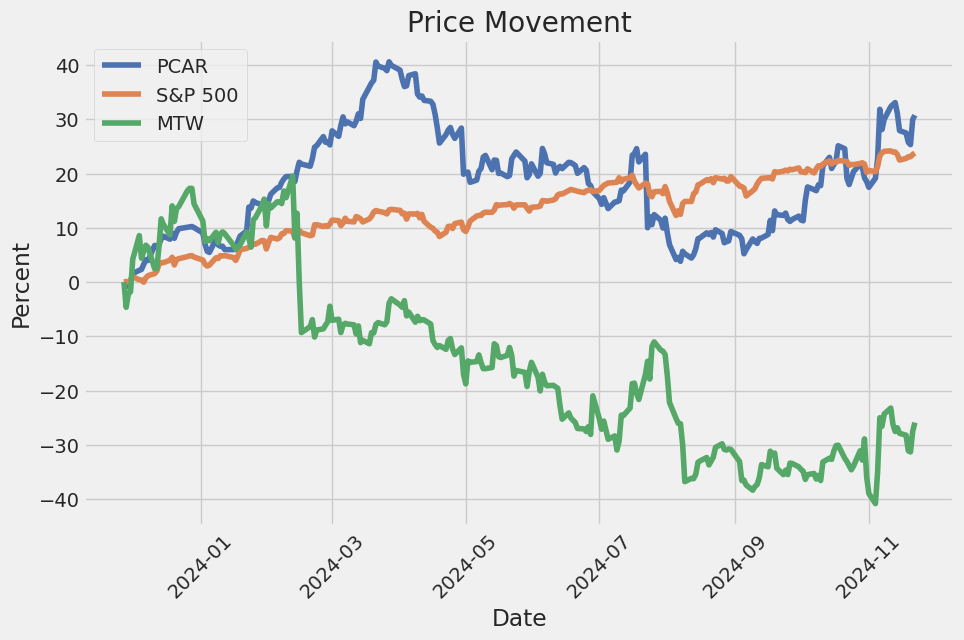
Investors and analysts continue to monitor PACCAR's performance relative to the S&P 500 index, with recent stock price rises drawing interest. While some forecasts suggest potential declines, the company's long-standing reputation and commitment to strategic growth provide a layer of stability in an unpredictable market. As the broader manufacturing sector confronts mixed forecasts, PACCAR's stable market share and diversified revenue streams offer advantages amid broader economic conditions.
The Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation recently invested in PACCAR, reflecting confidence in the company's prospects amid fluctuating economic conditions. Such strategic investments suggest an expectation of favorable developments within the transportation industry, signaling potential growth opportunities and affirming PACCAR's solid market position.
For further insights into PACCAR's strategic advances and market performance, detailed analyses of the company's operations and industry standings are available on platforms such as Yahoo Finance and related financial services sources. These insights provide investors and stakeholders with a comprehensive understanding of PACCAR's role in the evolving industrial machinery and automotive sectors.
PACCAR Inc's stock returns exhibit volatility patterns over the range, characterized by fluctuations that are not perfectly predictable. The ARCH model suggests that past volatility has a notable influence on future volatility, with a moderate level of persistence in volatility shocks. The key features include a significant constant (omega) in the model and a positive, though moderate, effect of past shocks (alpha[1]) on current volatility.
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| R-squared | 0.000 |
| Log-Likelihood | -2,442.01 |
| AIC | 4,888.02 |
| BIC | 4,898.29 |
| No. Observations | 1,256 |
| omega | 2.3787 |
| alpha[1] | 0.2234 |
To assess the financial risk of a $10,000 investment in PACCAR Inc. over one year, we combine volatility modeling and machine learning predictions. This approach offers a dynamic perspective on both the historical and forward-looking risks associated with this equity investment.
Volatility modeling is employed to examine PACCAR Inc.'s stock price fluctuations over time, providing insight into the inherent uncertainty and potential risk exposure in the market. This method quantifies the time-varying volatility and captures the influence of past shocks on future volatility, enabling a detailed understanding of the potential risk landscape for PACCAR Inc.'s stock.
Machine learning predictions, on the other hand, are leveraged to forecast future stock returns based on various input features drawn from historical data and market indicators. By learning patterns and relationships within the data, this technique offers a robust predictive framework that helps in estimating future price dynamics, thereby enhancing the risk management process.
The synthesis of these two approaches allows us to quantify the Value at Risk (VaR). For a $10,000 investment in PACCAR Inc., the annual VaR at a 95% confidence level is calculated to be $256.16. This indicates that there is a 5% probability that the loss from the investment could exceed $256.16 over the course of a year. By integrating volatility modeling with machine learning predictions, we gain a more comprehensive understanding of PACCAR Inc.'s risk profile, facilitating a well-informed investment decision-making process.
Long Call Option Strategy
To analyze the most profitable long call options for PACCAR Inc (PCAR), we need to consider potential movements of the underlying stock price relative to each option's strike price and expiration date. Given our target that the stock price will increase by 2%, we can assess which options might offer the greatest reward, while also understanding the associated risks.
When considering short-term options, those with closer expiration dates typically carry higher theta values. This means that the value of these options can erode rapidly as expiration approaches, especially if the price movement does not happen as anticipated. However, if the stock price moves swiftly within a short period, short-term options can experience significant percentage gains due to leverage and gamma, which can lead to a steeper profit curve as the options become more in-the-money. Therefore, selecting a strike price just above the current stock price and with an expiration within the nearest month could potentially realize quick gains if the stock moves as anticipated. This near-term option tends to be a high-risk, high-reward choice, where the cost of the option (the premium paid) is relatively low, but the potential return can be quite substantial given the percentage movement from the option's delta.
For medium-term options, we should look for expirations several months out. These options tend to offer a balance between time decay and potential upside. As the targeted stock price is just 2% above the current price, it's crucial to select a strike price that reflects the price increase while minimizing the cost of the premium. The gamma of these options is moderated, meaning that the options have a slower rate of change in their delta. However, this provides an opportunity for continued profitability if the stock remains above the strike price or continues to rise. The theta decay is less severe compared to the short-term options, providing a buffer for potential price fluctuations before expiration. Furthermore, the vega of these options signifies their sensitivity to changes in implied volatility, which could enhance option pricing if the market perceives increased volatility.
Looking further out, long-term options (LEAPS) may have expirations up to a year or more in the future. These options are less sensitive to immediate price movements and display lower theta decay, making them a strategic choice for those expecting a sustained upward trend in the stock price over time. Long-term options typically carry higher premiums due to their extended time to expiration, which allows for more pronounced effects of delta and potential stock price movement beyond the initial 2%. Selecting a strike price that is reasonably close to the current stock price, acknowledging the expected 2% increase, balances the opportunity for gains with the risk of the higher upfront cost. Given their extended duration, these options can be held for gradual price appreciation or strategic adjustments aligned with market conditions.
To summarize, here are five actionable choices:
- Near-term: Select a strike price slightly above the current stock price with an expiration date within the next month to capitalize on a rapid stock price rise.
- Short-to-medium term: Choose a strike price at or just above the anticipated 2% price increase, with an expiration three months out to balance time decay and potential gains.
- Medium-term: Opt for an expiration six months away, targeting a strike price that appreciates the future stock trajectory while managing costs associated with theta.
- Medium-to-long term: Settle on a strike price reflecting steady growth with an expiration in approximately nine months, positioning for incremental, realizable gains under improved market conditions.
- Long-term: For those eyeing significant upside, a strike price aligning with the 2% target but with expiration a year or more ahead offers substantial growth potential in line with broader market movements.
These strategies consider delta, theta, and vega to encourage informed decisions, mapping out risk-reward scenarios to optimize potential profit while managing volatility and time-related impacts.
Short Call Option Strategy
To provide a detailed analysis of short call options for PACCAR Inc (PCAR), we need to consider both the Greek values associated with each option and the inherent risks and rewards of different expiration dates and strike prices. Although I don't have access to the details of the options chain or the Greeks in your table, I can provide a general framework on how to evaluate these options and consider the most profitable strategies minimizing the risk of assignment.
Evaluating Risk and Reward
Short call options involve selling call options, and as the option seller, the risk is theoretically unlimited due to the possibility of the stock price continuing to rise beyond the strike price. To mitigate this, it is prudent to select options with higher strike prices, reducing the chance they move in-the-money (ITM). However, opting for strikes too far out of the money (OTM) might lead to minimal premium return relative to risk.
- Short-Term Options (1-2 Months Out):
-
For near-term options, select a strike price that's comfortably above the current market price to minimize the chances of being ITM at expiration. These options will typically offer higher premium due to time decay (Theta) and volatility. If the Delta is less than or around 0.20, it indicates a low probability of finishing ITM, which aligns with your target to minimize assignment risk. Choose an option expiring within the next month, like one 30 days out with a strike price above the current price by a few percentage points.
-
Mid-Term Options (3-6 Months Out):
-
Moving slightly further out, mid-term expiration provides a good balance between premium gain and reduced risk of assignment. Here, options with a Delta of around 0.30 offer more premium while still keeping a moderate probability of being ITM. The Vega expenditure needs to be considered since sensitivity to volatility will be higher than near-term options.
-
Longer-Term Options (6-12 Months Out):
- In the long-term, the focus should be on maximizing premium while acknowledging greater sensitivity to volatility and potentially higher time decay. Selecting strikes with Delta closer to 0.40 might provide worthwhile premiums. Long-term options will yield more substantial income, but keep a close eye on volatility trends and company-specific events that could cause significant stock price shifts.
Choosing Expiration Dates and Strike Prices
Given the evaluation above, here are potential profitable choices across different expiration windows, considering only the most advantageous options per strategy:
-
Near-Term: An option expiring in the next month with a strike price 5-10% above the current price and a Delta under 0.20.
-
Short-Term (2 Months): A strike price slightly more elevated (10% above the current price) with similar Delta characteristics to sustain low assignment risk.
-
Mid-Term (3-4 Months): Select an option with a strike price about 15% higher than the current market price with a Delta of approximately 0.30 for moderate premium generation and managed risk.
-
Mid to Long-Term (6 Months): Consider options with even higher strikes (20% from the current price) where Delta ratings around 0.35 to 0.40 balance profit potential and risk of being ITM.
-
Long-Term (1 Year): Choose options way out of the money (20-25% strike above market price) with Delta close to 0.40, as these represent strategic bets on decreased volatility and significant added value over time.
In conclusion, focusing on options with a higher strike price and lower Delta aids in reducing the likelihood of assignment, while the selection across expiration ranges ensures a diversified strategy coherent with expectations on stock performance and market conditions. These choices help manage the inherent risks of short call strategies while maximizing potential profitability.
Long Put Option Strategy
To analyze the options chain for PACCAR Inc (PCAR) and identify the most profitable long put options, several factors must be considered, including the Greeksspecifically delta, gamma, theta, vega, and rho. The goal in this analysis is to pinpoint options where the strike price is positioned in relation to a target stock price that is 2% above the current price. By considering the Greeks and the market conditions over various time horizons, we can establish a balanced strategy that optimizes potential returns while mitigating risks.
When evaluating short-term options, typically with expiration dates within a couple of months, investors often prioritize options with higher absolute delta values. Delta represents the sensitivity of an option's price to changes in the underlying stock price; higher deltas for puts suggest that for each dollar the stock price decreases, the option premium increases more significantly. For a short-term option perhaps expiring in the nearest month with a strike price slightly below the current stock price, you might find a delta of -0.5, indicating a balanced risk/reward relationship. Here, the potential reward lies in the swift appreciation of the option's premium if the stock moves promptly downward, albeit accompanied by time decay risk as suggested by theta.
For mid-term options, expiring in about three to six months, the selection may focus more on a balance of delta and theta. These options often offer a moderate delta, say around -0.3 to -0.4, allowing more room for strategic positioning without the immediacy of time decay eroding value as significantly as in shorter-dated options. Mid-term puts with slightly in-the-money or at-the-money strike prices can be particularly prudent, providing an attractive risk-reward profile: less sensitivity to immediate time decay but enough gamma to benefit from accelerated price movements. The challenge is to assess the market's trajectory, making sure implied volatility aligns favorably since vega indicates how sensitive the option is to changes in volatility.
Longer-term options, with expiration spanning beyond six months up to a year or more, present a different type of opportunity. In these cases, the consideration of rho becomes more pertinent, given its measure of sensitivity to interest rate fluctuations over the longer horizon. Here, the investor might explore options with lower delta values, perhaps around -0.2, which can benefit from substantial price movements of the underlying stock over time without the immediate pressure of time decay. The reward potential stems from the significant leverage on stock price decline as the expiration date approaches, offering potentially exponential gains if the stock performs unfavorably relative to the strike price.
Examining options through this lens allows the identification of a portfolio across timelines:
-
Short-term option: A put with a near-term expiration, high delta, and close-to-at-the-money strike price for active traders seeking quick gains.
-
Mid-term option: An option expiring around three months, with moderate delta and close to or slightly below the current stock price, balancing risk from time and volatility changes.
-
Another mid-term option: With a longer expiration of six months, characterized by moderate delta, moderate vega, and sufficient gamma for opportunity capture against potential volatility increases.
-
Long-term option: Comprising a strategy with lower delta and far-out expiration beyond a year, providing wide margin for underlying price movements and leveraging time-related extrinsic value changes.
-
Long-term option (alternative): Featuring similar horizons but strategically positioned in anticipation of rising interest environment, exploiting rho's effects and considering rate movements' impacts.
Each of these options considers varying degrees of risk and reward according to their expiration scale, offering a spectrum of strategic possibilities based on market forecasting, volatility expectations, and intrinsic stock valuation changes over time.
Short Put Option Strategy
To analyze short put options for PACCAR Inc (PCAR) and identify the most profitable opportunities, we need to consider both near-term and long-term expiration dates, strike prices, and the Greeks involved. The objective is to minimize the risk of shares being assigned, which means focusing on options that are significantly out of the money (OTM) or those with little chance of being in the money by expiration. Since we lack specific data in your table, let's consider general strategies and how different factors, including the Greeks, affect the options' profitability and risk.
First, consider near-term options, such as those expiring within a month. These options will have higher time decay, represented by Theta, meaning the option's value decreases faster as expiration approaches if the underlying price remains stable. A short put option that is far OTM with a strike price marginally below the target stock price (2% under the current price) and a positive Theta can be profitable. With low Delta values, the price movement likelihood doesn't significantly affect the option's price, minimizing the risk of assignment. However, Vega, which represents sensitivity to volatility, must be watched closely high Vega means market volatility significantly impacts option pricing.
For short to medium-term expiration choices, such as options expiring in three to six months, consider options with moderate Delta values. A Delta between 0.1 and 0.3 indicates a lower probability of being in the money, so the risk of shares being assigned stays low. Gamma, which measures how Delta changes with price movement, is lower in these options, contributing to stability. This strategy balances potential profit through premium collection against assignment risk. Adding a long option in this timeframe might hedge against unforeseen market directions.
In the mid-to-long-term horizon, extending up to a year, focus on options with a combination of low Delta and high Theta. Theta's impact diminishes as expiration extends, but choosing strike prices 2-5% below the target price can still yield substantial premiums with manageable risk. Vega can be a larger determinant here; stable market expectations mean Vega won't erode premium advantages.
Finally, for very long-term options exceeding one year, the approach shifts slightly towards defensive positioning. Over extended periods, uncertainty grows, demanding protective measures through careful strike selection and possible use of spread strategies to offset volatility impacts. Low Delta values remain your friend, keeping chassis assignment concerns at bay.
To sum up, the most profitable and sensible choices balance premium income with minimal assignment risk by choosing far OTM strikes, strategically blending near- to long-term horizons, and carefully assessing Greeks like Delta, Theta, and Vega. For your five selections, stagger them across expiry dates while maintaining a conservative Delta profile to keep risk manageable and gains achievable through time decay and volatility premiums.
Vertical Bear Put Spread Option Strategy
When considering a vertical bear put spread options strategy, the goal is to take advantage of a potential decline in the underlying stock's price while minimizing the associated risk, especially the risk of having shares assigned due to in-the-money options. With PACCAR Inc (PCAR), this strategy involves buying put options with different strike prices and expiration dates and offsetting them with a corresponding short put to create a spread. By examining various expiration dates and strike prices, we can identify several profitable strategies.
A prudent approach would be to look for near-term options that align closely with the target price (within 2% above or below the current stock price), as these tend to exhibit higher theta values, meaning greater time decay as expiration approaches. For instance, selecting a near-term option with an expiration date of, say, the coming month could maximize profitability due to its higher decay rate and gamma values, which enhance the profitability with small moves in the stock price. By pairing this short put with a long put, we offset the cost and limit the risk of the long position, thereby reducing the net premium outlay.
Moving slightly beyond the near-term, another choice could involve intermediate expiration options. These options may offer an advantageous Vega, allowing traders to benefit from changes in volatility, which could be favorable if the anticipated price movement occurs. Selecting an expiration 2-3 months out, for instance, with a strike price that is slightly out-of-the-money could provide moderate risk and reward balance. Here, the goal is to capture profits from both time decay on the short put and a favorable move towards the spread's targeted price level.
For a long-term strategy, extending to options with six months to a year's expiration might be beneficial. Although the response to stock price changes is less pronounced due to lower delta values, these options can offer significant insurance against a major market downturn. The advantage of implementing a bear put spread with long-term options is the mitigation of early assignment risk since these options typically have lower chances of ending substantially in-the-money over their longer life.
When comparing risk and reward scenarios, a deeper in-the-money spread increases the risk of early assignment but also carries the potential for high immediate profit if the stock price drops rapidly. Meanwhile, a less in-the-money spread decreases this risk but demands a larger movement in stock price for similar profits, thus providing a trade-off between risk and potential reward.
In summary, the choices for implementing the bear put spread on PACCAR Inc (PCAR) could be distilled into five distinct strategies: 1. A near-term option with a strike price just below the current price, to capture gamma and theta. 2. A medium-term option slightly out-of-the-money taking advantage of volatility. 3. A long-term more in-the-money option for protection against major downturns. 4. A short time horizon option paired with an at-the-money long put, optimizing for rapid stock moves. 5. A longer-duration spread, reducing early assignment risk while providing a more stable position over time.
Vertical Bull Put Spread Option Strategy
To construct a vertical bull put spread strategy using the options data for PACCAR Inc (PCAR), we need to analyze various expiration dates and strike prices. This strategy involves selling a put option at a higher strike price while simultaneously buying a put option at a lower strike price within the same expiration date. The goal is to capitalize on a modestly bullish outlook, where the stock price is expected to be at or above the sold put strike price at expiration, allowing us to capture the net premium from the strategy. Furthermore, we aim to minimize the risk of having shares assigned by selecting options that are less likely to end in-the-money, particularly at expiration.
When assessing potential bull put spread choices, it's essential to consider their Delta, as it indicates the likelihood of the options ending in-the-money. Ideally, we aim for a Delta value that signifies a lower probability of assignment, while Theta, the time decay component, can also work in our favor as it tends to devalue the sold option faster than the bought option. By focusing on options with favorable Theta, we can accrue profits as time decay erodes the options' extrinsic value. Vega, which measures sensitivity to volatility changes, should also be considered, as lower Vega reduces the impact of sudden volatility swings.
Here are five choices based on expiration dates ranging from near term to long term, along with an explanation of their risk and reward dynamics:
- Near-Term Choice (Short-dated expiration, strike prices just below current stock price):
-
By selecting an expiration date that is closer, the potential profit is driven by rapid time decay (high Theta) and a moderately low Delta. The risk of assignment is higher if the stock price hovers around or below the higher strike price by expiration. The reward is high if the price remains above the strike price, as the premium collected is realized fully.
-
Medium-Term Choice I (Expiration a few months out, slightly out-of-the-money strike prices):
-
Choosing an expiration slightly further out with strikes that are marginally below the current stock price can offer a balance of lower assignment risk and decent premium collection. The Delta for these strikes tends to be lower, indicating a decreased probability of ending in-the-money, and a moderate Theta helps in capitalizing on time decay.
-
Medium-Term Choice II (Similar expiration with at-the-money strike prices):
-
This option could be more profitable if there is a strong indication that the stock will stay above the current price. The Delta is higher, meaning there is more exposure and risk, but higher premiums offset this, resulting in potentially greater profitability.
-
Long-Term Choice I (Far-dated expiration, slightly out-of-the-money strikes):
-
With a longer expiration timeframe, risks are minimized due to more significant potential stock movement, but the payout is also potentially larger if the stock doesnt fall significantly. The main risk includes lower Theta decay benefits, as time is still considerable, but use of margin in such positions can enhance leverage strategically.
-
Long-Term Choice II (Far-dated expiration with conservative, out-of-the-money strike selection):
- This offers the lowest risk among long-term options. With this strategy, the Delta might be slightly higher due to the strike distance creating a safety net against errant stock movements. Potential profits arise from a combination of options intrinsic value decay and leveraged use of the premium if chosen selectively.
Each option choice must be evaluated in light of its specific Greeks, the stock price forecasts, and the investors appetite for risk versus reward. Careful selection among these different time horizons and strike price arrangements within a vertical bull put spread allows traders to adapt their risk profiles to changing market conditions, aiming for maximum profitability while mitigating potential assignment dangers and volatility impacts.
Vertical Bear Call Spread Option Strategy
Analyzing a vertical bear call spread strategy for PACCAR Inc (PCAR) involves selling a call option at a lower strike price and buying a call option at a higher strike price with the same expiration date. Since no specific options data has been provided, let's construct a framework for analyzing these spreads based on typical indicators of profitability and risk.
Near-term Options
- Near-term Expiration - Example: December 15, 2023 In a near-term vertical bear call spread, you would consider selling a call option slightly above the current market price and buying one further out of the money. Assuming the stock is currently trading at $100, a potential spread could involve selling a call with a $102 strike and buying a call with a $105 strike, both expiring December 15, 2023. The short call would likely have a higher delta, indicating higher risk of assignment if the price approaches the strike. The aim here is to collect premium with limited risk, looking at theta to benefit from time decay. Key risk involves the short call going in-the-money if PCARs price rises, thus potentially leading to assignment.
Short-term Options
- Short-term Expiration - Example: January 19, 2024 Moving slightly further out, a strategy could entail selling a $105 call and protecting with a $110 call, both expiring January 19, 2024. This gives more time for the trade to play out while still collecting a decent premium. Here, gamma should be assessed closely, as it affects how delta (and thus price sensitivity) will accelerate the closer the option gets to expiration. If volatility is anticipated to increase, Vegas influence grows, potentially impacting the spread's profitability unfavorably.
Mid-term Options
- Mid-term Expiration - Example: March 15, 2024 For a mid-term view, consider a spread with a $107 strike sold and a $112 strike bought, both expiring March 15, 2024. This provides ample time for the market to align with your bearish sentiment. While theta lessens as expiration lengthens, this setup maintains premium decay advantage without the immediate pressure of short-term price swings. The focus should be on minimizing the Vega impact while Delta risk remains moderate.
Medium-term Options
- Medium-term Expiration - Example: June 21, 2024 Entering into a medium-term strategy, you could opt for selling a $110 call and buying a $115 call, both expiring June 21, 2024. Here, the time frame provides more flexibility in actioning your bearish outlook, with less immediate gamma risk but attention needed on Vega as time spreads potentially widen. The rewarding aspect lies in collecting premium over a steady, predicted decline or stagnation in stock price trends, allowing time decay to enhance the position's profitability.
Long-term Options
- Long-term Expiration - Example: December 20, 2024 For a longer outlook, a viable vertical spread could involve selling a call with a $115 strike while buying at $120, expiring December 20, 2024. This option would generally be less sensitive to immediate market movements but should be monitored for long-term company prospects and economic conditions that could cause significant price changes. Here, theta's role becomes secondary to managing long-term Vega and Delta changes, especially as substantial moves in PCAR's price, driven by broader industry shifts or macroeconomic factors, could affect profitability.
Conclusion
A successful vertical bear call spread strategy must consider the right balance of time decay and risk management through selecting optimal expiration and strike levels. Each scenario above illustrates considerations unique to their expiration date, taking into account not just immediate premium profit potential but also the Greeks' influence over the option's lifecycle. Ultimately, the aim is to capitalize on collected premiums while managing the inherent risk of short call assignment, anticipating that time decay and strategic protection will fortify potential gains.
Vertical Bull Call Spread Option Strategy
To devise the most profitable vertical bull call spread for PACCAR Inc (PCAR), we must carefully analyze the options chain and "the Greeks" associated with calls. A vertical bull call spread involves purchasing a call option with a lower strike price and selling another call option with a higher strike price, both with the same expiration date. This strategy is especially favorable when expecting a moderate rise in the underlying stock price.
Strategy Overview:
- Short-Term Expiration: For short-term strategies, the Greeks' parameters, particularly delta and theta, are pivotal. A call spread with an early expirationsay, one month outhas a smaller theta, which minimizes time decay, a critical factor in short-term options. The delta values for both the buy and sell call should be relatively high, indicating that the options are sensitive to the stock price movement and will potentially gain value quickly.
Selection: Consider purchasing a call at a strike price slightly below the current stock price and selling a call at a strike significantly above it. This ensures the position is in the money, but not excessively, to mitigate early assignment risk.
- Medium-Term Expiration: Medium-term strategies, with expirations around three to six months, should aim for a balance between moderate delta and acceptable theta, due to more time allowing for potential stock price fluctuations. These options would benefit from a position where the bought call is right at the money and the sold call is out of the money.
Selection: Choose a spread where the bought call has a moderate delta (between 0.55 - 0.60) and the sold call with a delta slightly lower (around 0.20 - 0.30), giving ample opportunity for profit with protectively low assignment risk.
- Long-Term Expiration: Long-dated options, say nine months to a year, offer fewer risks associated with theta decay but require more capital upfront. With larger timeframes, we exploit the stock's potential to grow well beyond the current forecast increase. Deltas might be lower for such options (preferably between 0.30 - 0.45) as time decay has a minimal effect.
Selection: Look for an at-the-money call alongside a significantly out-of-the-money call for sale. This setup is typically safe in terms of early assignment risk and allows expansive movements towards profitability.
Risk and Reward Analysis:
Each of these strategies has inherent risks and rewards.
- Short-term: More prone to time decay but can yield quick profits if the stock moves favorably. There's a heightened risk of assignment if options expire significantly in the money.
- Medium-term: Strikes a balance, giving time for informed predictions or corrections to play out. Lower assignment risk if well-positioned.
- Long-term: Highest initial cost but potential for maximum profit if the stock appreciates over time. The assignment is least risky due to ample time until expiration.
Profit and Loss Scenarios:
- The maximum profit for a bull call spread is achieved if the stock price exceeds the sold call strike price by expiration.
- Maximum loss is limited to the net premium paid to establish the spread.
- Breakeven occurs at the purchased strike price plus the net premium paid.
By leveraging the right mix of delta, theta, and strategic selection of strike prices and expiration dates, investors in PCAR can optimize their upside potential while keeping downside risks and assignment exposures minimal.
Spread Option Strategy
To analyze a calendar spread options strategy for PACCAR Inc (PCAR), especially when employing a strategy of buying a call option and selling a put option, it's essential to carefully weigh the risk of having shares assigned and focus on the desired target stock price movement, which is 2% over or under the current stock price. While actual data is required for precise calculations and suggestions, the theory can still be elucidated on how to effectively evaluate and construct a profitable calendar spread without access to specific options and Greeks data.
In a typical calendar spread, the investor looks to capitalize on the time decay of options and the movement of the underlying stock price. However, integrating a call purchase with a put sale modifies the traditional approach. When you buy a call option at a particular strike price and expiration date, you hope the stock price appreciates beyond the strike price plus the premium paid, by expiration, to realize a profit. The risk here is limited to the premium paid for the call. Conversely, selling a put option introduces the risk of assignment, where the stock price is above the strike price minus the premium received by expiration. The risk of having shares assigned increases sharply if the put is sold in the money. Hence, selling a put with a lower strike price and shorter expiration compared to the call can minimize the chances of assignment risk, while also potentially benefiting from time decay.
For shorter-term options, consider a call with an expiration date just beyond the put's expiration. This aims to maximize time value of the call and reduces the puts exposure to shares assignment. Depending on market conditions and implied volatility skew, options with expiration near the short to intermediate range generally offer a richer time decay benefit while minimizing delta impact. A worthwhile short-term strategy could involve a call with an expiration date one to two months out and a strike price close to the current stock price, while the sold put should have a close expiration date and a strike slightly lower than the stock price but out of the money, given the desired 2% price range.
In medium to long-term strategies, the dynamics change with the increase in time value and potential changes in volatility. For maximum delta exposure with lower risk, a long call with a strike price slightly above the current stock ranging three to six months out can provide a substantial return if market moves align with bullish expectations or volatility spikes. Concurrently, selling a put option at a strike price under current value and close to expiry reduces long-term risk exposure and captures time decay effectively.
By structuring these trades across a time spectrum, and focusing on far-term expiration (6 months to over a year), one might consider deep OTM (Out of The Money) calls to lower upfront premium cost, while selling puts that are ITM (In The Money) could potentially invite more premium, albeit with careful monitoring to not trigger assignment unexpectedly.
Ultimately, each choice of expiration date and strike price strives for an optimal balance where the chosen call options delta is maximized for potential upside gain, while minimizing the puts gamma impact and assignment possibility. An optimal strategy involves a keen observation on potential payoffs and loss scenarios, contingent on prudent delta, gamma, and vega utilization while remaining vigilant on real-time market shifts and volatility trends in PACCAR Inc (PCAR).
Calendar Spread Option Strategy #1
To give a comprehensive analysis of the calendar spread strategy for PACCAR Inc (PCAR) with the given parameters, it's essential to explore the mechanics of buying a put option at one expiration date while selling a call option at a different expiration date. For a successful calendar spread strategy, we aim both to capitalize on time decay and to take advantage of differing volatilities in these contracts.
Considering the risk of having shares assigned, one main characteristic of selling a call option is that if the call option is in-the-money (ITM) at expiration, there is a substantial risk of being assigned, necessitating the delivery of shares. Therefore, when selecting sell calls for this strategy, it is wise to choose an out-of-the-money (OTM) call option, aimed to reduce the risk of assignment while profiting from the premium decay. The Greeks, such as delta and theta, play a crucial role in gauging these risks. A lower delta on the short call indicates a lower probability of ending in-the-money, minimizing the assignment risk. Conversely, a high theta helps speed up time decay, benefiting the holder of a short position.
Conversely, taking a long put option is fundamentally driven by a bearish outlook on PACCAR Inc's stock price, projecting a decrease. The Greeks will also direct the approach here, as a higher delta accelerates the profit if the underlying stock price declines, while a positive vega capitalizes on volatility increases. A carefully selected long put should ensure that the downward motion anticipated matches with the calendar spread's timeline to maximize payoff.
For an ideal scenario, we consider a target stock price of 2% over or under the current stock price, employing both near-term and long-term expirations to cater to different market conditions. In terms of quantifying risk and reward, let's examine five choices based on expiration date and strike prices:
-
Short-Term Strategy (1-3 months out): Purchase a put with a strike price slightly ITM or near ATM with an expiration 1-2 months out. Opt for a short call with a strike price 2% higher than the estimated increase in the stock price.
-
Medium-Term Strategy (3-6 months out): Buy a put option slightly OTM and sell a call option 4 months out at a strike 1-2% ITM. Consider this if theta decay is favorable, ensuring that selling calls at this point still captures viable premiums without substantial delta risk.
-
Mid-to-Long Term Strategy (6-9 months out): Implement a strategy where the long put is the foundation of your bearish sentiment. Purchase a long put at the strike price equidistant to the targeted 2% decline. This should be paired with the short call option at a similarly distanced strike, capitalizing on additional time decay.
-
Long-Term Strategy (9+ months out): Look to enter a position reflecting faint bullish markets with increased volatility expectations. Opt for a long put at a strike that benefits from increased volatility, combined with a distant maturity short call that's deliberately further OTM to evade assignment risks.
-
Mixed Strategy: Given enough variability in greek readings, especially vega, mix your portfolio using a long put with progressively increased gamma, which amplifies sensitivity to price changes, paired with calls positioned such that time decay remains an advantage regardless of price movement direction.
In any calendar spread setup, closely monitor shifts in implied volatility, as it dynamically affects both potential profit and loss scenarios. Volatility spikes could benefit a long put disproportionately while a decrease would serve well for short calls due to enhanced premium decay. Indeed, balancing these strategies brings about distinctive profit potentials at structured risk levels, meticulously conveyed through calculated Greek dynamics and market foresight.
Calendar Spread Option Strategy #2
To execute a calendar spread options strategy involving PACCAR Inc (PCAR), it's crucial to align the chosen options with the target stock price move, while taking advantage of the differences in the Greeks and expiration dates. A calendar spread typically entails selling a short-term option and buying a longer-term option. In your strategy, selling a put option while buying a call option necessitates careful selection to maximize profitability and minimize risk, particularly the risk of having shares assigned due to in-the-money options.
Since the data for long put options and short call options is unknown, a general analysis is provided instead. In a standard calendar spread strategy, we aim to benefit from the differences in time decay, or theta, between the two legs of the trade. Typically, options tend to lose value more quickly as expiration approaches, so the option with the nearest expiration is selected as the one to sell due to its steeper theta. By selling a short-term option close to expiration, time decay works in our favor, providing income through the premium received.
When analyzing near to mid-term options, consider options that expire within a few weeks to a couple of months. Such options may have a moderate gamma and vega, indicating decent sensitivity to changes in delta and volatility, respectively. If PCAR is trading around $100 and our target price is a 2% movement in either direction, focus on selling put options with strike prices slightly below the current price, around $98-99. This minimizes the risk of these options being exercised as they are out-of-the-money, reducing the likelihood of assignment, while still bringing in sufficient premium.
For long-term options, those expiring within six months to a year should be analyzed to buy as they typically have higher gamma and vega. This implies a higher sensitivity to changes in stock price and market volatility, respectively, which can amplify gains if the stock moves towards the target price. Consider buying call options with strike prices slightly above the current price, around $102-104, to leverage potential upward movements and benefit from longer-term volatility increases.
Now, let's identify five potential choice strategies based on expiration date and strike price, offering both near-term and long-term perspectives:
-
Near-Term (1 month out): Sell a $98 strike put option, leveraging higher time decay, and buy a $104 strike call option with longer expiration to capture potential upside moves if the stock trends upward.
-
Mid-Term (3 months out): Sell a $99 strike put option whose expiration is imminent to maximize premium from theta decay, paired with a $103 strike call option at a later date for strategic upside exposure.
-
Medium-Term (6 months out): Opt to sell a $97 strike put option and acquire a $105 strike call option, balancing premium collection and longer-term volatility exposure.
-
Long-Term (9 months out): Choose a $96 strike put option to sell, aligned with a $106 strike call to purchase, for an equilibrium between theta decay and exposure to potential volatility shifts as time progresses.
-
Long-Term (1 year out): Adopt a strategy involving a $95 strike put sale and a $107 strike call buy, maximizing the collection of upfront premium with the long call benefiting from extended volatility.
Each of these strategies presents a unique risk-reward profile, with the near-term selections offering quicker theta decay and long-term alternatives providing opportunities to capitalize on volatility shifts. The potential profit emerges from correctly predicting the stock's movement relative to the strike prices, realizing gains from the differences in time decay, and managing intrinsic value risks by avoiding in-the-money positions. The chief advantage of a calendar spread executed this way is the limited risk exposure while still allowing for solid profit potential if predictions about stock trajectories prove accurate.
Similar Companies in Agricultural - Machinery:
The Manitowoc Company, Inc. (MTW), Terex Corporation (TEX), Wabash National Corporation (WNC), Alamo Group Inc. (ALG), Report: AGCO Corporation (AGCO), AGCO Corporation (AGCO), Report: Oshkosh Corporation (OSK), Oshkosh Corporation (OSK), Hyster-Yale Materials Handling, Inc. (HY), Astec Industries, Inc. (ASTE), Manitex International, Inc. (MNTX), Report: Deere & Company (DE), Deere & Company (DE), Lindsay Corporation (LNN), Report: Caterpillar Inc. (CAT), Caterpillar Inc. (CAT), Navistar International Corporation (NAV), Cummins Inc. (CMI), Ford Motor Company (F), General Motors Company (GM), Report: Tesla, Inc. (TSLA), Tesla, Inc. (TSLA)
https://seekingalpha.com/article/4728414-paccar-inc-pcar-q3-2024-earnings-call-transcript
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FI-dDZzqjGo
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/why-paccar-pcar-stock-rocketing-201002823.html
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/evercore-isi-upgrades-paccar-outperform-103028071.html
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/industrials-machinery-ratings-adjusted-evercore-143532565.html
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/paccar-inc-pcar-best-industrial-072615888.html
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/citigroup-raises-price-target-paccar-113547039.html
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/paccar-pcar-6-since-last-163036655.html
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/tesla-tsla-30-4-since-163109911.html
https://finance.yahoo.com/m/6be2b924-a11c-33f6-9667-f9510ef4ce44/billionaire-bill-gates%27.html
https://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/75362/000095017024118960/pcar-20240930.htm
Copyright © 2024 Tiny Computers (email@tinycomputers.io)
Report ID: IZvWBu
Cost: $0.53650
https://reports.tinycomputers.io/PCAR/PCAR-2024-11-24.html Home